
Environmental impact is the alteration or modification caused by human action on the environment. Today, there are many terms related to the impact on the environment of different materials or products used on a daily basis.
In order to understand the effect that different materials generate in the natural environment, it is necessary to know the following concepts:
Eco-Friendly
This term is used for those products or materials that have been specifically developed to reduce their environmental impact. It can also be applied when reducing negative parts for the environment in the manufacturing processes of a product or material.
Sustainable
Sustainability refers to the action of humans to meet their current needs without compromising or negatively affecting future generations. A sustainable process is one that ensures economic growth while caring for the environment and social well-being.
Fillamentum Timberfill wood fibre filaments, extract the filling fibres from their filaments from controlled felling forests. These forests operate in such a way that an ever smaller volume is extracted annually than the volume growing in the forest, i.e. always more trees have to be planted than are felled.
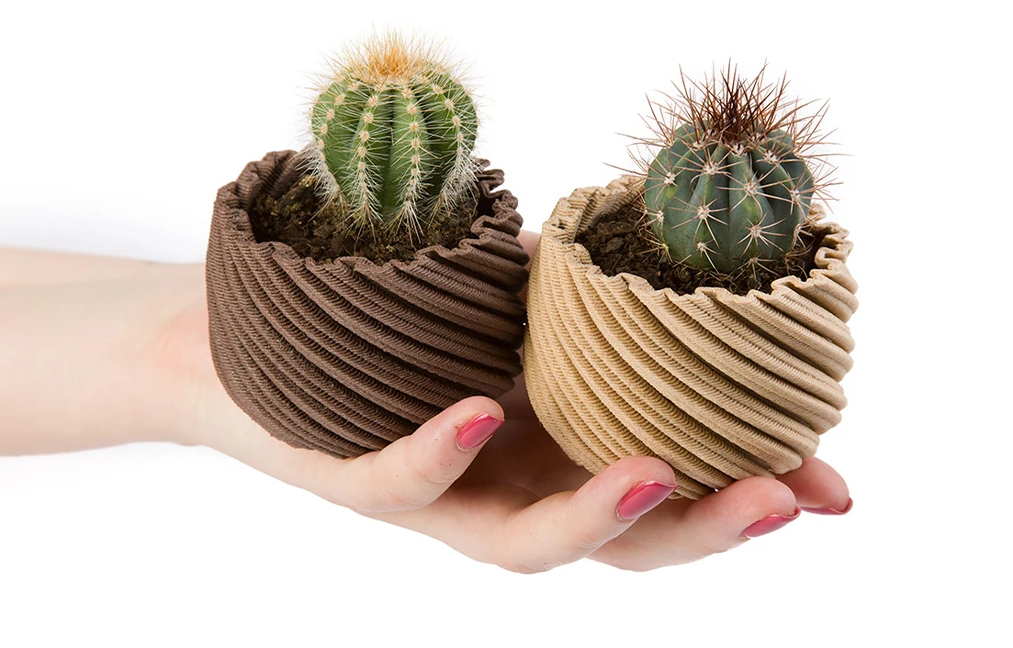

Image 1: Parts printed with Timberfill filaments. Source: Fillamentum.
Biodegradable
A material or product is said to be biodegradable when it is degraded by the action of biological agents and environmental conditions of a certain type in a certain period of time. The time of biodegradation can vary greatly depending on the composition of the material and the environmental conditions.
In the field of 3D FDM printing, PLA is a biodegradable material. This material is one of the most widely used in the field of 3D printing because of its properties and ease of use. It is also one of the most commonly used materials as a binder in biocomposite filaments.
Bioplastics
Another concept to be considered is that of Bioplastics, also called organic plastics. Bioplastics are natural polymers that are not derived from petrochemicals but from renewable sources. These plastics are generally biodegradable.
An example of a biodegradable bioplastic is PLA, which is made from starch extracted from corn, beets and wheat.
Compostable
When a material can decompose in less than 90 days without leaving toxic residues, becoming useful matter (compost), it is considered compostable. A compostable material will always be biodegradable, while a biodegradable material does not have to be compostable. The composting process consists of the accelerated degradation of organic matter by a microbial population in a humid, warm and aerobic environment under controlled conditions. Composting can be done at the household level, using a home compost pile or composter, or at the industrial level, when it is done in composting plants.
Biocomposite
A biocomposite is a composite material consisting of a matrix (resin) and a natural fibre filler. The matrix can be made up of polymers derived from renewable resources (such as PLA) or non-renewable resources.
The natural fibre filler can act as a reinforcement, improving the mechanical properties of the material, or provide aesthetic properties to the material by its colour or texture. Natural fibres can be fibres from crops such as hemp, wood, paper waste or crop by-products such as cellulose.
Concern for the environment has led to the research and development of specific biocomposite materials for 3D FDM printing. Among our products, you can find the C2composites range of biocomposite filaments, based on PLA and filled with hemp fibres (Entwined), beer waste (Buzzed), coffee waste (Wound Up) or organic waste (Landfilled).
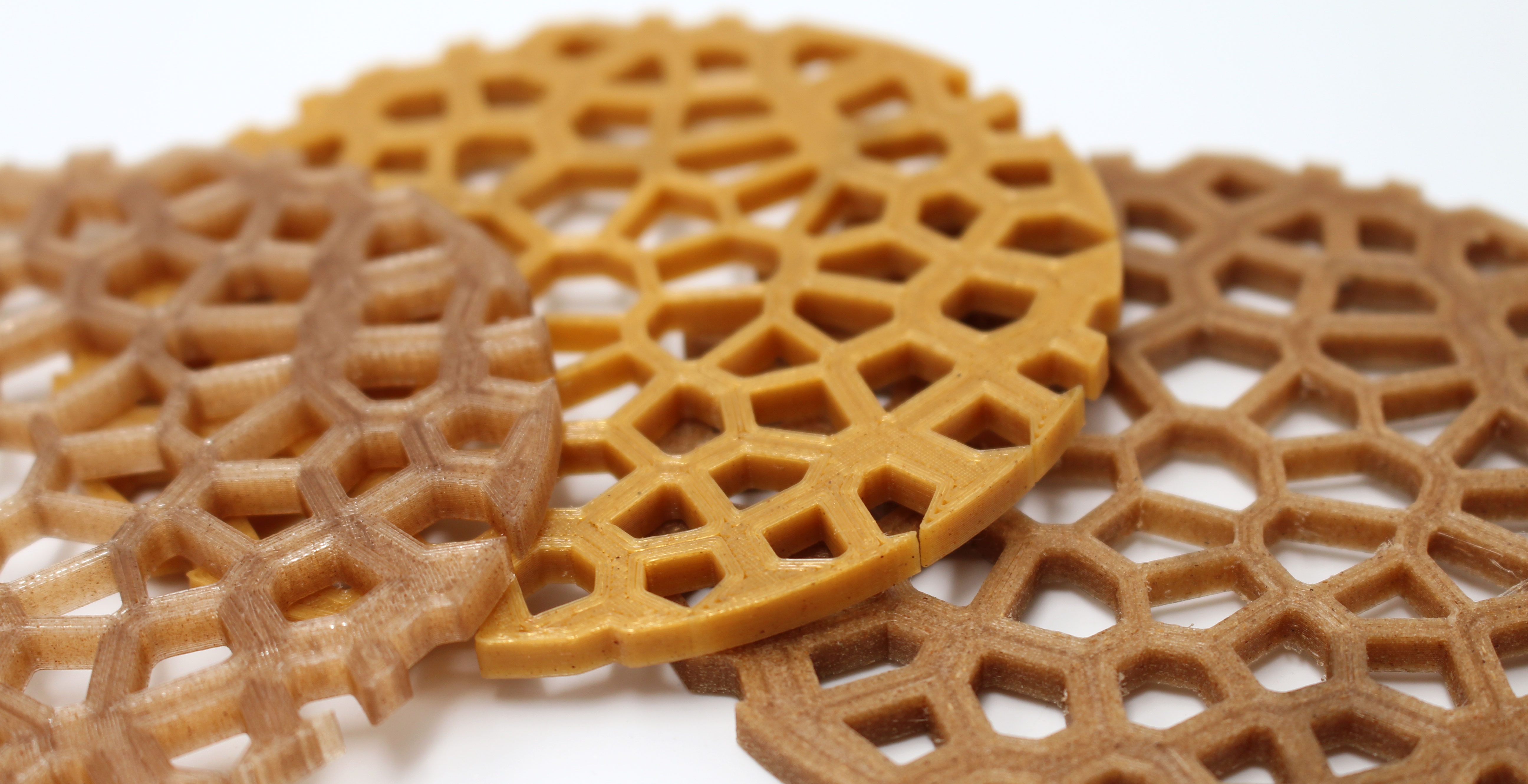

Image 2: Pieces printed with the Wound filament Up™, Entwined™ and Buzzed™. Source: Filament2print.
Recyclable / Recycling
Recycling is a process whose objective is to convert waste into new products or raw materials for later use. Recycling prevents the disuse of potentially useful materials, reduces the consumption of new raw materials, and in many cases also reduces energy use, air and water pollution, and the emission of greenhouse gases.
A material is recyclable when it can be useful after its main use, thanks to a recycling process. A recyclable material does not necessarily always become the same material, ready for use again. Sometimes materials are recycled by taking advantage of the value they still have, for example, to generate energy.
A material is said to be recycled when it comes from the recycling of materials or products. Recycling is an interesting option in the development of 3D FDM printing materials. An example of this is Formfutura's recycled filaments: Reform rPLA. These filaments are produced from PLA extrusion waste streams that are recomposed and homogenised into high quality PLA filaments.
.jpg)
Image 3: Manufacturing cycle of Reform rPLA. Source: Formfutura.
Reused
The concepts of "Recycle" and "Reuse" are often confused. Recycling requires a treatment or process that starts from an initial material to obtain another material or the same again. However, in reuse, the product is used or adapted for use in another application without requiring a recycling process.
For example, in our article "Ideas for reusing empty filament coils" we list different options for reusing the coils once the filament is finished.

Image 4: Storage system. Source: Cults3D.
The search for materials with low environmental impact has encouraged various initiatives and the development of new 3D printing materials, leading to the production of innovative filaments with mechanical properties that resemble those of ABS, or with representative characteristics or physical properties that differentiate them from other materials; using techniques such as recycling to create a new filament, or loading natural fibres to produce biocomposite filaments.
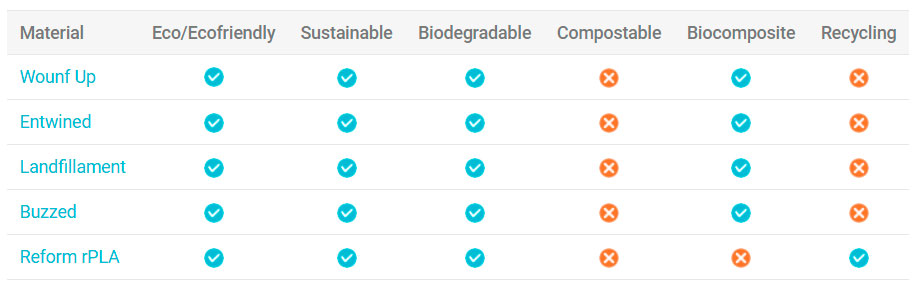
Some of these innovative materials can be found in our catalogue. The following table shows what qualities each of them has.
| Material | Eco/Ecofriendly | Sustainable | Biodegradable | Compostable | Biocomposite | Recycling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wound Up | ||||||
| Entwined | ||||||
| Landfillament | ||||||
| Buzzed | ||||||
| Reform rPLA |






Thank you. I got satisfying information for filament
Thank you. I got satisfying information for filament google.com
Thank you. I got satisfying information for filament-

Carol Abbott
dic 22, 2020
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) is an increasingly popular material among users of 3D FDM/FFF printers due to the production of the Advanced ABS. https://crackedlink.com/idm-crack-key-free-download/ Every consumer knows that PLA is the most commonly used, and that ABS is the most widely used 3D printing material for making resistant and usable elements, from basic parts to parts that are subject to mechanical stress, but both have some disadvantage; ABS is vulnerable to warping when mostly large parts are made.
Related posts
Which filament dryer should you choose?
abr 02, 2024Top 5 brands of CNC machines and laser cutters/engravers
ene 15, 2024High speed FDM 3D printing with supports
nov 22, 2023Raise3D introduces the DF2 Solution at Formnext
nov 14, 2023Gadgets, games and crafts with FDM 3D printing
jun 21, 2023Zetamix in laboratories: microwave sintering
jul 05, 2023